In some parts of the world, electricity transmission and distribution systems are over one hundred years old, but a host of digital and physical technologies are turning them into “digital grids of the future.” This transformation couldn’t come soon enough. The World Economic Forum reports that using digital technologies to optimize the grid could bring society up to $1.2 trillion in value. The smart pairing of these emerging digital technologies with the conventional physical and digital tools already available in the grid bring about an opportunity to transform these systems in critical ways, such as:
The latter two outcomes, while economically powerful, also bring with them the added benefit of reducing the environmental impact associated with electricity production and delivery. Digital grid technologies have the potential to reduce electricity-related carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions in the United States by up to 12 percent by 2030, according to a report by the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. If this number is scaled globally, that’s equivalent to reducing global CO2 emissions by 2 billion metric tons per year by 2030. This is the same carbon impact as taking 1 million passenger cars off the road—about half of the passenger cars in use globally.
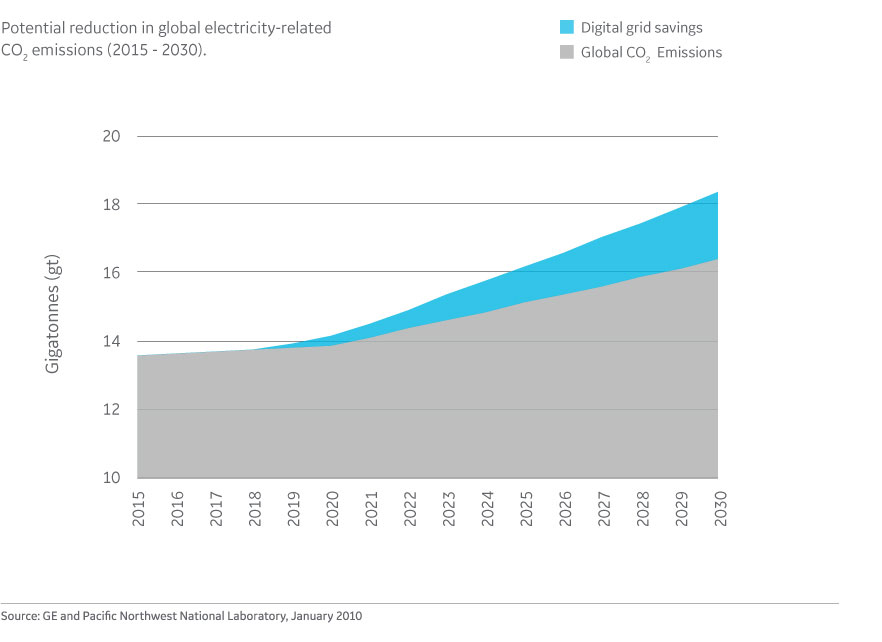
Figure 1: The Potential Impact of the Digital Grid
These benefits are accomplished through a smarter, more aggressive operation of the grid by taking advantage of a much better understanding of the current state of the network. These tools do not reside in singular locations of the grid; instead they are stitched together into solutions that deploy the right intelligence throughout all levels of the grid. The intelligent fabric that extends from control systems on generation assets, through utility operations centers, and into a new and powerful cloud resource is the digital grid, and it is an essential part of the energy ecosystem of the future.
This is an important time for the energy industry, as the world accelerates its embrace of clean and renewable energy resources, distributed energy resources and electric vehicles to power its development and growth. In the middle of this transformation lies the grid, the true enabler that receives this clean energy and routes it to end-users. The nature of the grid has already started to change, moving away from a sole bulk transport mission to more broadly balancing power across regions as renewable energy production shifts geographically and temporally throughout the day. How the grid evolves, both physically and digitally, will determine how economical the transformation to these cleaner energy resources is, and will therefore be a factor in the speed at which they are adopted.
Connecting the coming new renewable energy resources to the grid will require significant investments in transmission and distribution infrastructure. To make these investments economical, it is imperative that they include thoughtful consideration to the way that the grid is operated, making the best use out of the flexibility of installed and new assets to compensate for the variability of these resources. Moreover, these investments should cast a wide net in looking at the tools to be deployed for realizing expansion of the power delivery capacity. Non-wires alternatives, coupled with a deeper and faster intelligence, can allow significant growth in capacity to come from within the infrastructure already deployed, as well as to help new infrastructure to be sized with an expectation of higher performance.
The emerging digital grid is a big leap forward in helping to improve the efficiency and carbon footprint of energy systems at a time when environmental sustainability is critically important for people and the planet. To learn more about these new digital tools and their transformative potential, we invite you to read our new report “The Digital Grid and the Environment.”